Cisco Catalyst 3500 Xl Ios
Cisco Network Topologies and LAN Design Foundation TopicsDo I Know This Already Quiz. The questions in the following quiz are designed to help you gauge how well. Compare your answers with those. Appendix A, Answers to Quiz Questions. If you answer most. Q A and Case Studies. If you find you need to review only certain. Q A and Case Studies questions. If. you find the following questions too difficult, read the chapter carefully until. Q A and Case. Studies questions. Hi I have a catalyst 3500 series XL switch with current Version 12. WC1, MAINTENANCE INTERIM SOFTWARE on it. Is there any new ios release I can. This chapter from CCDA Exam Certification Guide reviews the topologies used in network design and covers the technologies and design approaches used when designing. Cisco Catalyst 3500 Xl Ios DownloadWhat OSI layer does a bridge operate The 1. Base. 2 Ethernet media is commonly referred as What is the recommended maximum number of nodes that should be. Sound Of Uk Garage Rar'>Sound Of Uk Garage Rar. LAN segment Bridges control collision domains, broadcast domains, or. What is the maximum segment size in a 1. Base. T network What is the maximum segment size in a 1. Base. 2 network Routers operate on what OSI layer Fast Ethernet is covered by which IEEE standard What is 1. Base. 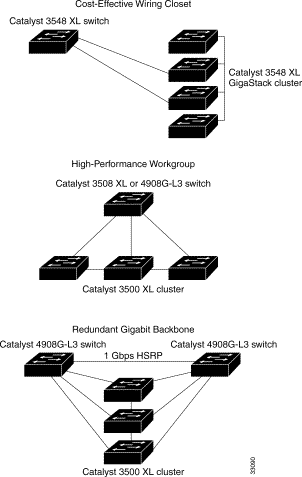 Cisco Catalyst 3500 Xl Iosemus
Cisco Catalyst 3500 Xl Iosemus This document addresses the Frequently Asked Questions FAQs on the Quality of Service QoS features of the Catalyst 2900 XL and 3500 XL series switches. This. What device controls a broadcast domain You can find the answers to these questions in Appendix A, Answers to. Quiz Questions. LAN Topology Design. The CCDA objectives covered in this section are as follows 1. Describe the advantages, disadvantages, scalability issues, and applicability. Draw a topology map that meets the customers needs and includes a. This section covers CCDA exam objectives about designing network topologies. LAN. LANs provide data transfer rates that are typically much faster. WANs. While most companies own their own LAN. LANs are usually leased on a. With the recent developments in Gigabit. Ethernet technologies, LAN designs are now capable of 1. Mbps speeds. High speed Gigabit links can connect servers to LAN switches. At these speeds. the capacity is there to meet the performance requirements of current. Various speeds of Ethernet have evolved into the de facto standard for LANs. Ethernet uses a contention based access method, meaning each device competes. All devices attached to the same. Ethernet segment form a collision domain. Each device transmitting on that. As the number of devices in the same. Although not discussed in newer switched bridged networks, legacy Ethernet. To scale multiprotocol networks and networks with high bandwidth applications. This. is covered in the section LAN Hardware later in the chapter. Three different network topology models are discussed in the following. Hierarchical models. Redundant models. Secure models. Hierarchical Models. Hierarchical models enable you to design internetworks in layers. To. understand the importance of layering, consider the Open System Interconnection. OSI reference model, which is a layered model for implementing computer. Using layers, the OSI model simplifies the tasks required for. Hierarchical models for internetwork design also. Each layer can be. Hierarchical models apply to both LAN and WAN. Benefits of Hierarchical Models. The many benefits of using hierarchical models for your network design. Cost savings. Ease of understanding. Easy network growth. Improved fault isolation. After adopting hierarchical design models, many organizations report cost. The modular nature of the model enables appropriate use of bandwidth. Keeping each design element simple and small facilitates ease of. Management. responsibility and network management systems can be distributed to the. Hierarchical design facilitates changes. In a network design, modularity. As each element in the network design requires. In large, flat, or meshed network architectures. Improved fault isolation is facilitated by structuring the network into. Network managers can easily understand the. Todays fast converging protocols were designed for hierarchical. To control the impact of routing overhead processing and bandwidth. EIGRP. Route summarization is facilitated by hierarchical network design. Route. summarization reduces the routing protocol overhead on links in the network and. Hierarchical Network Design. As Figure 4 1 illustrates. The core layer provides optimal transport between sites. The distribution layer provides policy based connectivity. The access layer provides workgroupuser access to the network. Figure 4 1 A. Hierarchical Network Design Has Three Layers Core, Distribution, and Access. Each layer provides necessary functionality to the network. The layers do not. Each layer can be. A particular layer can be omitted altogether, but for optimum. Core Layer. The core layer is the high speed switching backbone of the network, which is. The core layer should have the. Ware Weather Fax Frequencies. Offer high reliability. Provide redundancy. Provide fault tolerance. Adapt to changes quickly. Offer low latency and good manageability. Avoid slow packet manipulation caused by filters or other. Have a limited and consistent diameter. NOTEWhen routers are used in a network, the number of router hops from edge to. As noted, it is considered good practice to. This means that. from any end station to another end station across the backbone, there should be. The distance from any end station to a server on the. Limiting the diameter of the internetwork provides predictable performance. Distribution layer routers and client LANs can be. Distribution Layer. The distribution layer of the network is the demarcation point between the. The distribution layer can have many. Policy for example, to ensure that traffic sent from a particular. Security. Address or area aggregation or summarization. Departmental or workgroup access. Broadcastmulticast domain definition. Routing between virtual LANs VLANsMedia translations for example, between Ethernet and Token. RingRedistribution between routing domains for example, between two. Demarcation between static and dynamic routing protocols. Several Cisco IOS software features can be used to implement policy at the. Filtering by source or destination address. Filtering on input or output ports. Hiding internal network numbers by route filtering. Static routing. Quality of service mechanisms for example, to ensure that all devices. Access Layer. The access layer provides user access to local segments on the network. The. access layer is characterized by switched and shared bandwidth LANs in a campus. Microsegmentation, using LAN switches, provides high bandwidth to. Ethernet segments and reducing the. Token Ring LANs. For small officehome office SOHO environments, the access layer provides. WAN technologies. ISDN, Frame Relay, and leased lines. Features such as dial on demand. DDR and static routing can be implemented to control costs. Hierarchical Model Examples. For small to medium sized companies, the hierarchical model is often implemented. Figure. 4 2. Corporate headquarters forms the hub and links to the remote offices. Figure 4 2 The. Hierarchical Model Is Often Implemented as a Hub and Spoke Topology. You can implement the hierarchical model by using either routers or switches. Figure 4 3 is an. Figure. 4 4 shows examples of routed hierarchical designs. Figure 4 3 An. Example of a Switched Hierarchical Design. Figure 4 4 Examples. Routed Hierarchical Designs. Redundant Models. When designing a network topology for a customer who has critical systems. Consider incorporating one of the following types of redundancy into your. Workstation to router redundancy. Server redundancy. Route redundancy. Media redundancy. Each of these types of redundancy is elaborated in the sections that. Workstation to Router Redundancy. When a workstation has traffic to send to a station that is not local, the. Address Resolution Protocol ARPExplicit configuration.
This document addresses the Frequently Asked Questions FAQs on the Quality of Service QoS features of the Catalyst 2900 XL and 3500 XL series switches. This. What device controls a broadcast domain You can find the answers to these questions in Appendix A, Answers to. Quiz Questions. LAN Topology Design. The CCDA objectives covered in this section are as follows 1. Describe the advantages, disadvantages, scalability issues, and applicability. Draw a topology map that meets the customers needs and includes a. This section covers CCDA exam objectives about designing network topologies. LAN. LANs provide data transfer rates that are typically much faster. WANs. While most companies own their own LAN. LANs are usually leased on a. With the recent developments in Gigabit. Ethernet technologies, LAN designs are now capable of 1. Mbps speeds. High speed Gigabit links can connect servers to LAN switches. At these speeds. the capacity is there to meet the performance requirements of current. Various speeds of Ethernet have evolved into the de facto standard for LANs. Ethernet uses a contention based access method, meaning each device competes. All devices attached to the same. Ethernet segment form a collision domain. Each device transmitting on that. As the number of devices in the same. Although not discussed in newer switched bridged networks, legacy Ethernet. To scale multiprotocol networks and networks with high bandwidth applications. This. is covered in the section LAN Hardware later in the chapter. Three different network topology models are discussed in the following. Hierarchical models. Redundant models. Secure models. Hierarchical Models. Hierarchical models enable you to design internetworks in layers. To. understand the importance of layering, consider the Open System Interconnection. OSI reference model, which is a layered model for implementing computer. Using layers, the OSI model simplifies the tasks required for. Hierarchical models for internetwork design also. Each layer can be. Hierarchical models apply to both LAN and WAN. Benefits of Hierarchical Models. The many benefits of using hierarchical models for your network design. Cost savings. Ease of understanding. Easy network growth. Improved fault isolation. After adopting hierarchical design models, many organizations report cost. The modular nature of the model enables appropriate use of bandwidth. Keeping each design element simple and small facilitates ease of. Management. responsibility and network management systems can be distributed to the. Hierarchical design facilitates changes. In a network design, modularity. As each element in the network design requires. In large, flat, or meshed network architectures. Improved fault isolation is facilitated by structuring the network into. Network managers can easily understand the. Todays fast converging protocols were designed for hierarchical. To control the impact of routing overhead processing and bandwidth. EIGRP. Route summarization is facilitated by hierarchical network design. Route. summarization reduces the routing protocol overhead on links in the network and. Hierarchical Network Design. As Figure 4 1 illustrates. The core layer provides optimal transport between sites. The distribution layer provides policy based connectivity. The access layer provides workgroupuser access to the network. Figure 4 1 A. Hierarchical Network Design Has Three Layers Core, Distribution, and Access. Each layer provides necessary functionality to the network. The layers do not. Each layer can be. A particular layer can be omitted altogether, but for optimum. Core Layer. The core layer is the high speed switching backbone of the network, which is. The core layer should have the. Ware Weather Fax Frequencies. Offer high reliability. Provide redundancy. Provide fault tolerance. Adapt to changes quickly. Offer low latency and good manageability. Avoid slow packet manipulation caused by filters or other. Have a limited and consistent diameter. NOTEWhen routers are used in a network, the number of router hops from edge to. As noted, it is considered good practice to. This means that. from any end station to another end station across the backbone, there should be. The distance from any end station to a server on the. Limiting the diameter of the internetwork provides predictable performance. Distribution layer routers and client LANs can be. Distribution Layer. The distribution layer of the network is the demarcation point between the. The distribution layer can have many. Policy for example, to ensure that traffic sent from a particular. Security. Address or area aggregation or summarization. Departmental or workgroup access. Broadcastmulticast domain definition. Routing between virtual LANs VLANsMedia translations for example, between Ethernet and Token. RingRedistribution between routing domains for example, between two. Demarcation between static and dynamic routing protocols. Several Cisco IOS software features can be used to implement policy at the. Filtering by source or destination address. Filtering on input or output ports. Hiding internal network numbers by route filtering. Static routing. Quality of service mechanisms for example, to ensure that all devices. Access Layer. The access layer provides user access to local segments on the network. The. access layer is characterized by switched and shared bandwidth LANs in a campus. Microsegmentation, using LAN switches, provides high bandwidth to. Ethernet segments and reducing the. Token Ring LANs. For small officehome office SOHO environments, the access layer provides. WAN technologies. ISDN, Frame Relay, and leased lines. Features such as dial on demand. DDR and static routing can be implemented to control costs. Hierarchical Model Examples. For small to medium sized companies, the hierarchical model is often implemented. Figure. 4 2. Corporate headquarters forms the hub and links to the remote offices. Figure 4 2 The. Hierarchical Model Is Often Implemented as a Hub and Spoke Topology. You can implement the hierarchical model by using either routers or switches. Figure 4 3 is an. Figure. 4 4 shows examples of routed hierarchical designs. Figure 4 3 An. Example of a Switched Hierarchical Design. Figure 4 4 Examples. Routed Hierarchical Designs. Redundant Models. When designing a network topology for a customer who has critical systems. Consider incorporating one of the following types of redundancy into your. Workstation to router redundancy. Server redundancy. Route redundancy. Media redundancy. Each of these types of redundancy is elaborated in the sections that. Workstation to Router Redundancy. When a workstation has traffic to send to a station that is not local, the. Address Resolution Protocol ARPExplicit configuration.